Training
Our Success Stories
CIGL’s Training Models
-
Training Model for Entrepreneurship
a) To inspire and empower young entrepreneurs to cultivate entrepreneurship in all the sectors of the Ghanaian economy.
b) To provide trainees with comprehensive knowledge about Agribusiness, including its various aspects such as production, marketing, value addition, and sustainability.
c) To educate business owners on the various financing options available for Agribusiness ventures, including grants, loans, and investment opportunities, and guide on accessing these resources.
-
Models and Descriptions
Youth Entrepreneurial Skills Development & Enterprise Development
Introduction to entrepreneurship, business awareness/start your own business, business growth programme, customer care, vocational skills & management training (for informal sector operators), corporates
Starting a New Business
Business Idea and Business Opportunity Seeking for Informal Business. Forming a new Company, developing new products like Car washbasins, Sachet water producers, and sources of funding, and managing early operations of SMEs.
Enterprise Coaching & Mentoring
Market studies and research. Business Diagnosis and Health Checks, Business Counseling, Feasibility Studies and Business Plan Preparation, Client Accounting and Book-keeping Service (CABS), Corporate restructuring and turnaround, Logistics support for Workshops.
Access to Sustainable Finance
Sources of Finance both local and international, Factors influencing the choice of sources of Finance and identification of Startups costs. Sources of Finance both local and international, Factors influencing the choice of sources of Finance and identification of Startups costs.
Tit-bits of Corporate Governance & Enterprise Management Waste Management
People’ management, organizational structure, strategy formulation, internal controls, policies and procedures, financial Risk, Operational risk, reputational risk, etc.
Production process design, Effectively developing proper waste management control projects. Health and Safely needs, Environmental sustainability.
Retirement & Pensions
Pension and contribution towards retirement.
-
Training Model for Financial Literacy for Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
1) Understand the principles of financial literacy. 2) Know the components of financial literacy.
3) Know the importance of being financially literate, and the drawbacks of not being financially literate.
-
Models and Descriptions
Introduction to Financial Literacy
Keeping business records, sources of finance (how to access funds for business), making money works in business, financial management.
Financial Planning & Budgeting
- Setting Financial Goals
- Creating a Financial Plan
- Creating a Budget
- Expense Tracking
- Adjusting and Revising
Savings & Investments
Setting Financial Goals
- Emergency Fund
- Regular Saving Habits
- Understanding Investment Options
- Risk Management
- Diversification
Credit & Debt Management
- Understanding Credit
- Responsible Borrowing
- Improving Credit Score
- Debt Repayment Strategies
- Debt Consolidation
Avoiding Debt Traps
Tax Planning
- Basic Tax Knowledge
- Tax-Efficient Strategies
Financial Products & Services
- Investment Products
- Insurance Products
- Banking Services
-
Training Model for Financial Literacy for Financial Institutions (FIs)
a) Design, develop and implement non-trivial financial instruments and processes relevant to emerging financial sectors to boost profitability. b) Appreciate the creation of innovative financial instruments and processes that can be achieved by a professionally crafted agile financial reengineering that will maximize market value while minimizing cost of capital.
c) Identify, analyse and assess risk, and its mitigation processes to help protect the organization from market threats and competitors.
d) Understand products and services restructuring hands-on; that offers innovation strategies and techniques such as increasing or reducing risk, pooling risk, swapping income streams, and splitting income streams that connect long-term obligations into short-term ones in financial institutions.
e) Explore the external economic environment where banks operate (financial markets) and interact with dynamic corresponding target customers to improve performance, profitability and strategic direction.
-
Models and Descriptions
Financial Reengineering
- Identify Basic Fixed Income Securities
- Non-trivial financial instruments development and implementation
- Restructuring and financial engineering perspectives
- Redesign of core financial changes and improvements in capital structure
- Introduction to Derivative Securities The mechanics of forwards, futures, swaps and options.
Risk Management
- Different sources and types of credit risk
- Principles of Risk Management and Insurance
- Optimization of credit risk management, profitability and liquidity position of a Bank
- The role and importance of Asset Liability Management (ALM) in Banking
- Apply and critique a range of techniques used to manage financial market risk
Information Technology Risk Management
- The cyber threat landscape and key drivers of cyber Risk
- Cyber Risk Management & Practices
- Cyber Risk regulations & Risk Supervision
- Introduction to Decision Support Syteme & Knowledge Management
-
Training Model for Agriculture Lending
1) To make a business case for agricultural finance as a tool for sustainable economic development.
2) To draw the distinction between traditional agricultural financing versus agricultural value chain financing.
3) To apply the tools applicable in agricultural production and value chain financing.
4) To leverage on the various Risk Mitigation tools to encourage financing to the agriculture sector.
-
Models and Descriptions
Agriculture and Agribusiness Environment of Ghana
- The Principles and Practice of Lending to Agricultural Value Chains
Agribusiness Appraisal Techniques
- Identifying and Managing Risks in Agricultural Value Chain Financing
- Financial Statement Analysis
Managing Agribusiness Loan Portfolio
- Agriculture and Agribusiness Environment of Ghana
- Making A Business Case for Agribusiness Financing
- Managing Agricultural Credit Risk
- Setting Credit Policies and Procedures for Agribusiness Lending
- Agriculture and Agribusiness Environment of Ghana
- Making A Business Case for Agribusiness Financing
- Managing Agricultural Credit Risk
- Setting Credit Policies and Procedures for Agribusiness Lending
- Agricultural Loan Portfolio Management Techniques and Problem Loans Strategy
- Data Reporting and Loan Administration
- Participants undertake Farm/ Enterprise visit
-
Training Model for Corporate Governance
a) Strengthening the knowledge of the participants about good governance and the various development programmes and discussing the issues and mechanisms for the effective delivery to working masses.
b) Inform corporate constituencies, other than investors and shareholders, that have specific economic ties to the corporate entity to evaluate potential conflicts of interest, deter corruption, and increase public confidence in government/businesses.
c) Raise the awareness of act of behaving honorably, even when no one is watching so as to extend to professional areas at work such as decision-making, interacting with colleagues and serving customers or clients.
-
Models and Descriptions
Corporate Governance & Leadership
- The Role of a Board
- An Audit Committee’s Responsibilities
- ESG and Shareholder Engagement
- Strategic Management for Change Leadership
Financial Disclosures & Corporate Governance
- Dynamics of corporate governance
- Corporate governance and money
- Boardroom integrity and financial adequacy
Board Integrity And Ethics
- Ethics of Board Selection & financial integrity
- Reporting Breaches of Financial Integrity
- Board structures & Processes
- The purpose, strategy & Vision, Values & standards for the business
Training Model for Project Finance
- Ethics of Board Selection & financial integrity
- Reporting Breaches of Financial Integrity
- Board structures & Processes
- The purpose, strategy & Vision, Values & standards for the business
-
Training Model for Project Finance
a) To develop the cognitive, pschomotor and affective domain of participants to understand the techniques that managers/stakeholders can used to raise huge amounts of capital in both developed and developing countries for the foreseeable future.
b) To acquire three competence skills as operational, professional, and strategic competence skills.
-
Models and Descriptions
Overview of Project Finance
- Introduction to project finance
- Uses for project finance
- Why use project financing
- Description of a typical project finance transaction
- Parties to a project financing
- Financing sources used in project financing
Project Structure and Participants
- Debt & equity Issues
- Developers and consultants
- Sponsors, off-takers, operators
- The role of law firms, consultants, construction and engineering firms
- Activities of political and regulatory bodies
Understanding Key Project Risks
- Entity risks and Transaction risks
- Mitigating and managing project risks
- Security and Insurance issues
- Project Cash Flow Analysis and mitigation strategies.
- General Considerations of Credit Risk Appraisal.
Evaluating The Project
- The offering/ Information memorandum issues
- Legislation relating to information memoranda
- Legal Aspects in Project Finance
- Project Agreements


Some Training Sessions
Training Session and the Set Ups
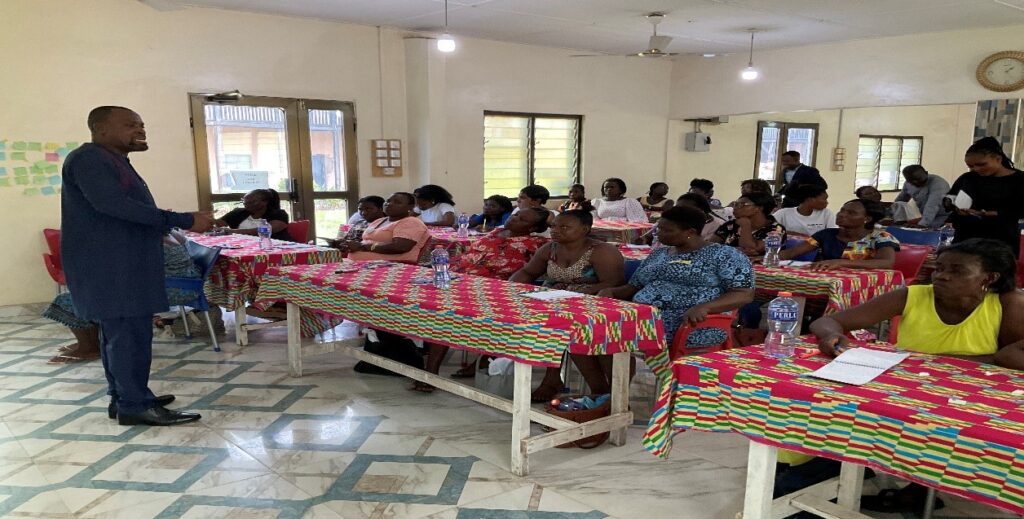
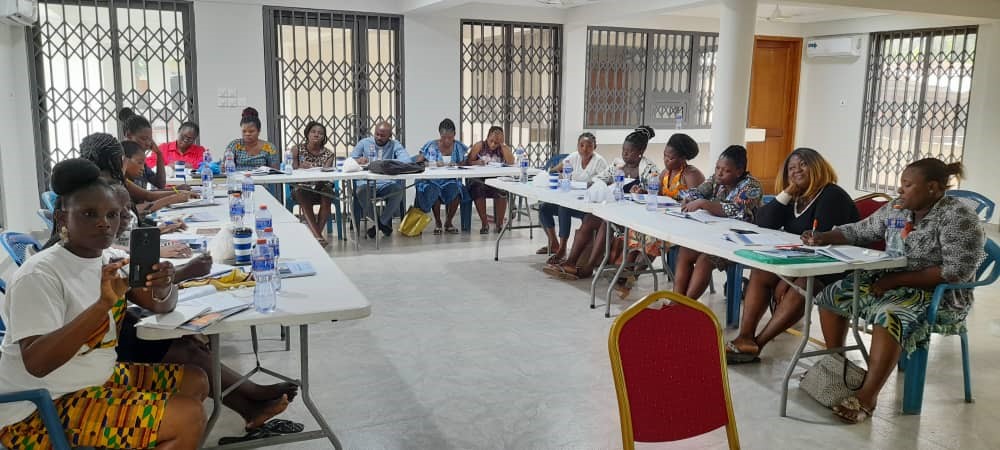
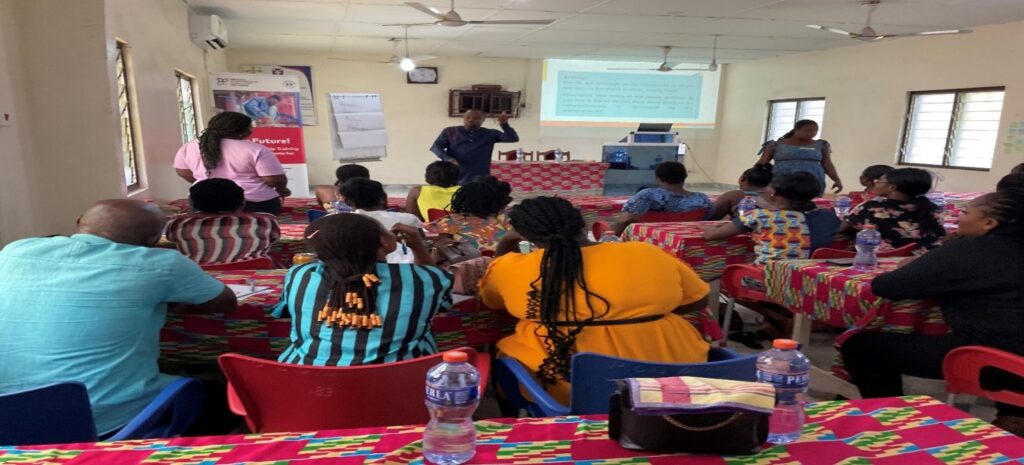



Our Group Sessions
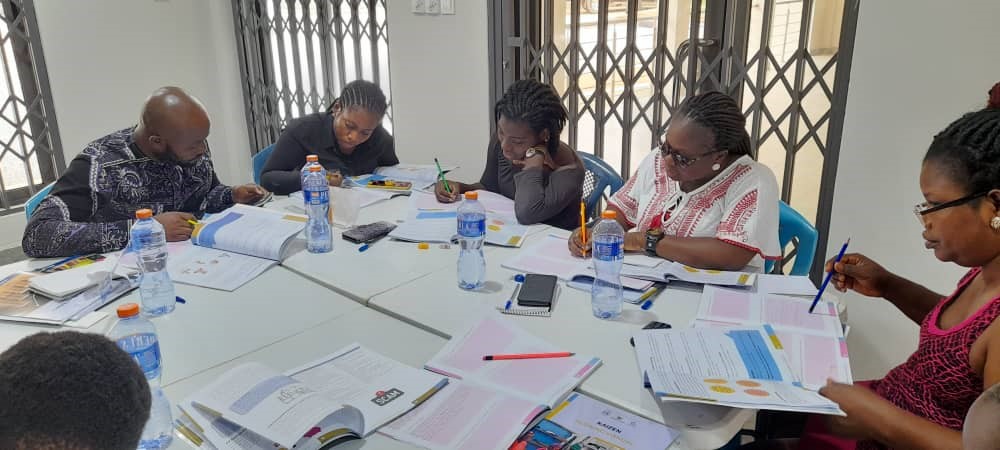
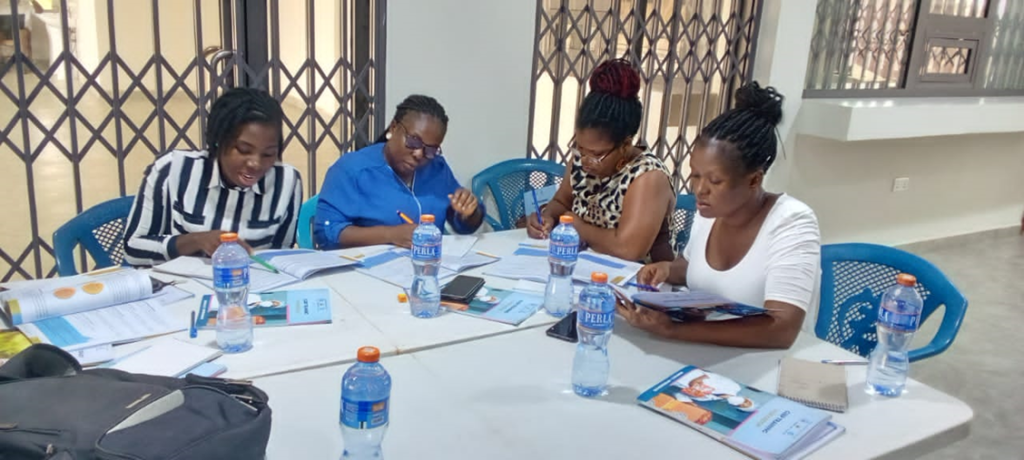
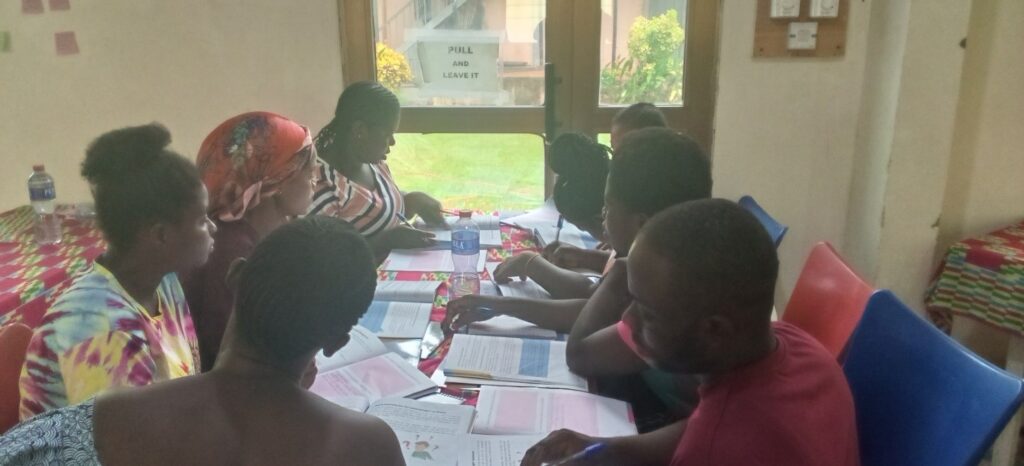



Our Group Sessions
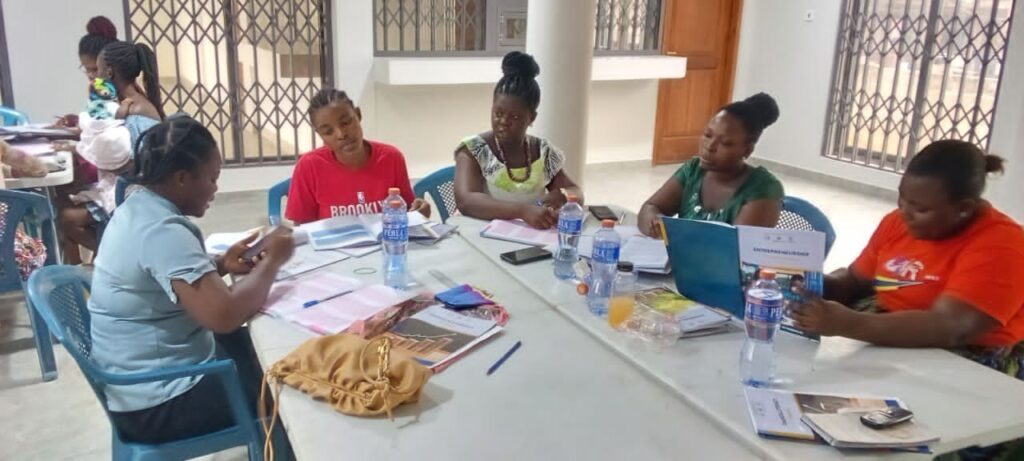
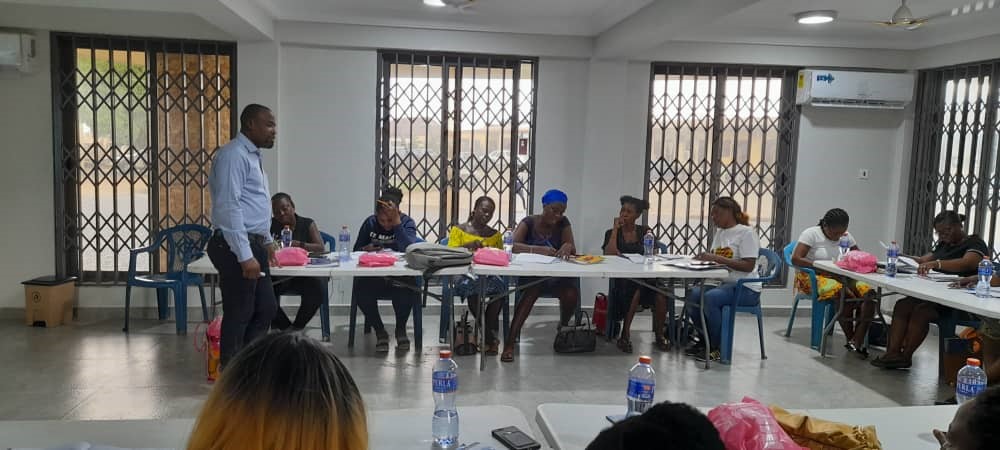
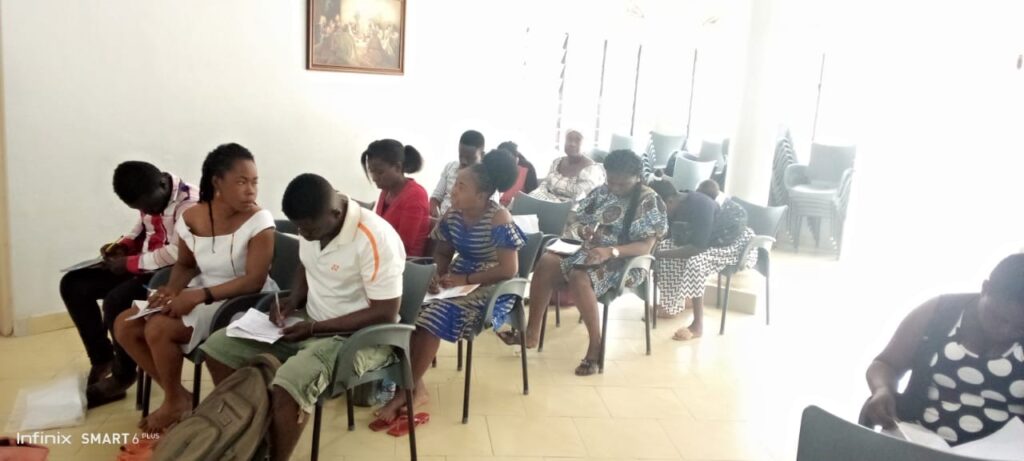






Moment of Pitch Practice
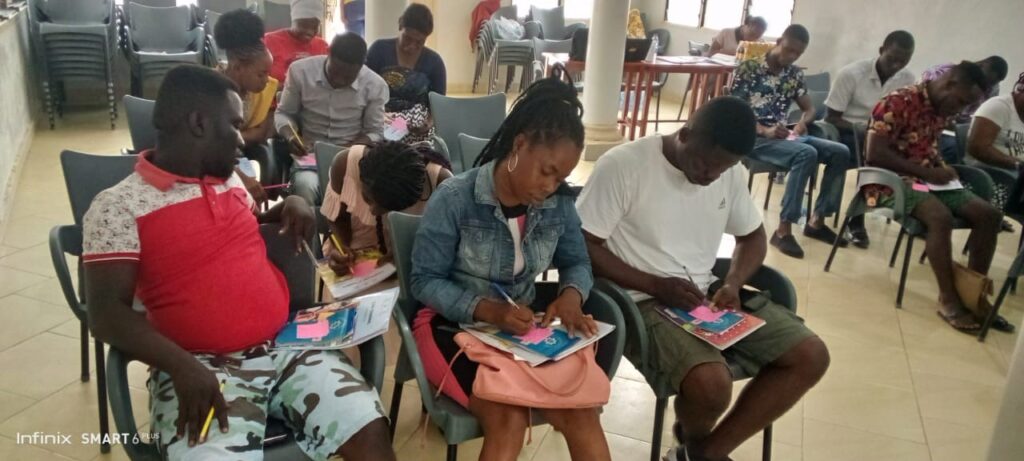
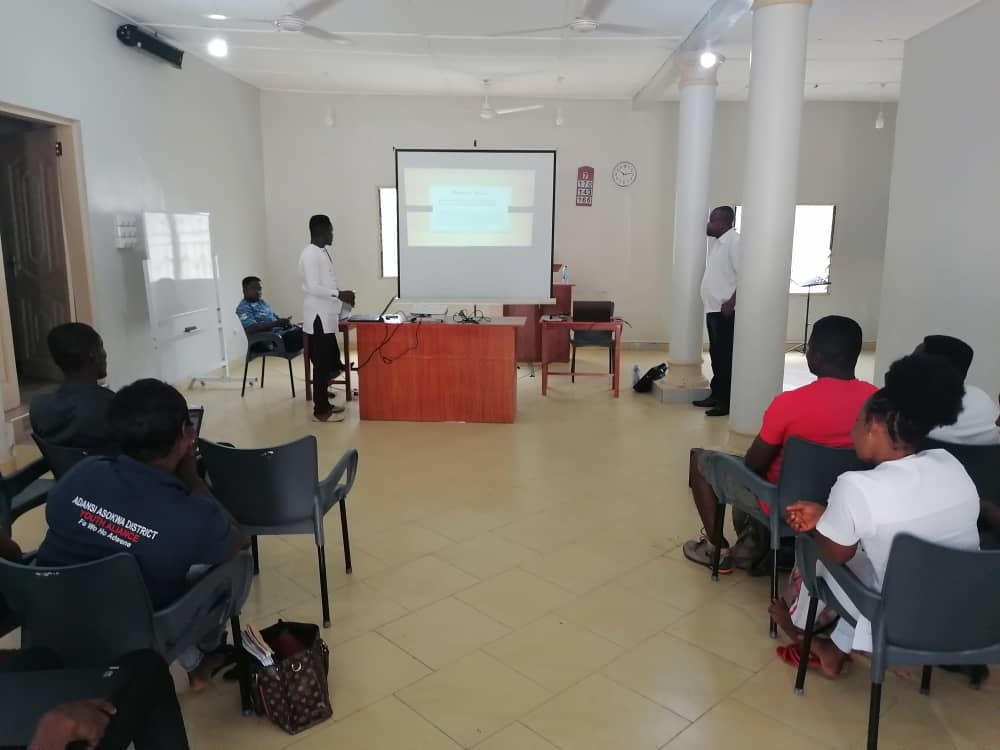


Peer Mentorship Sessions
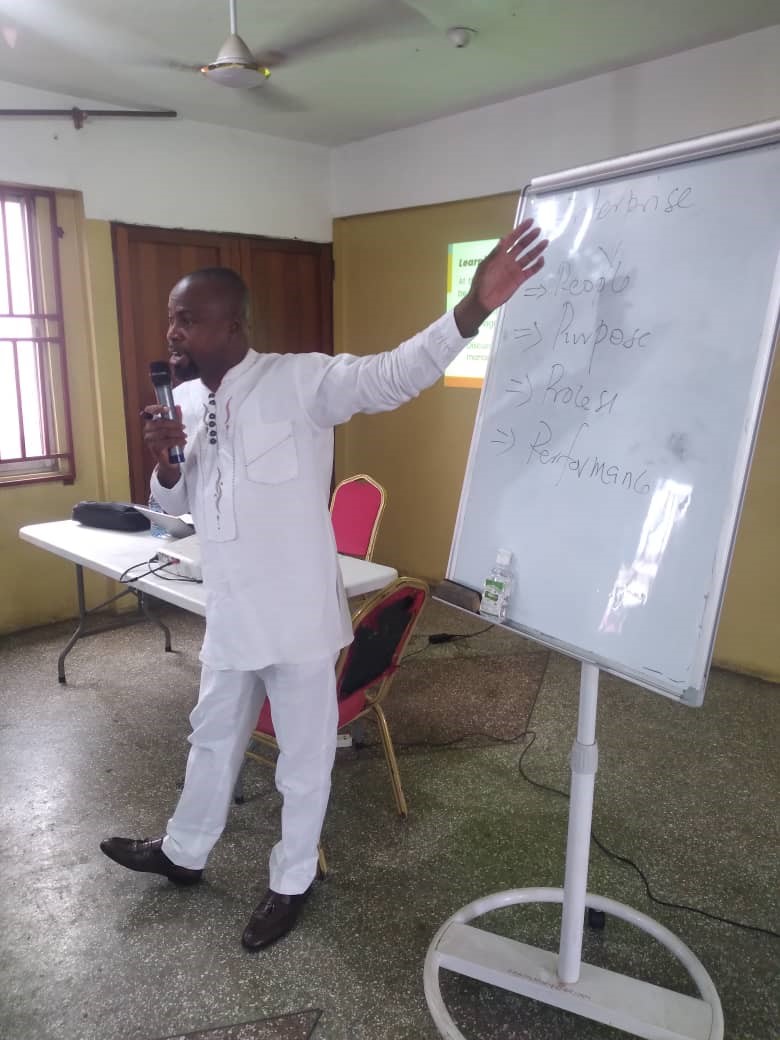
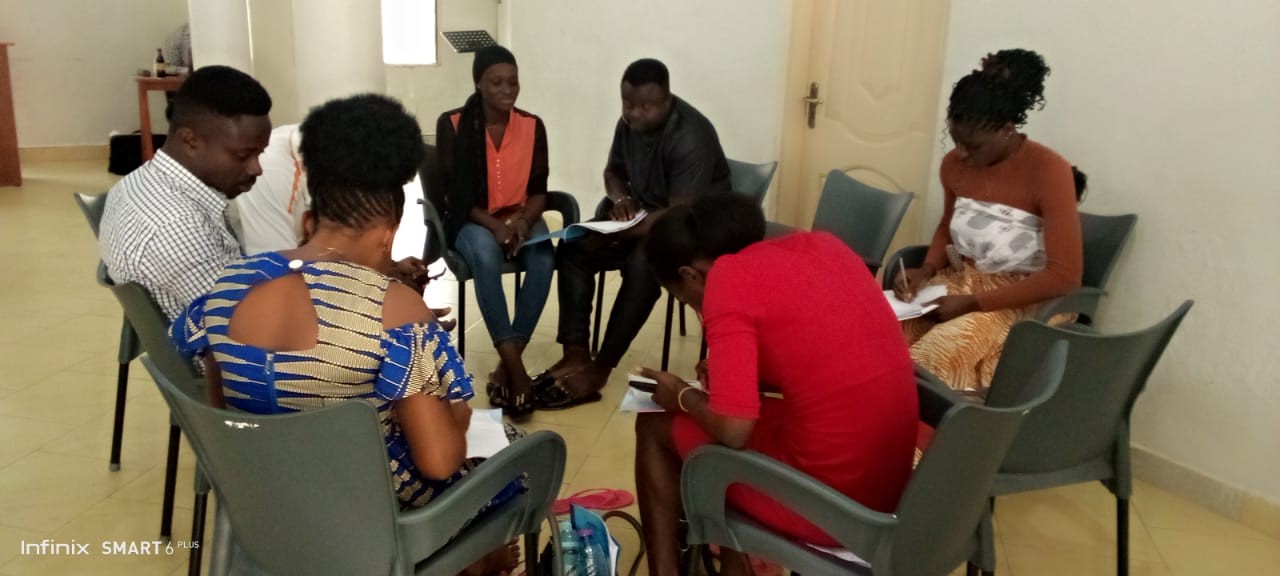


The Facilitation Moments
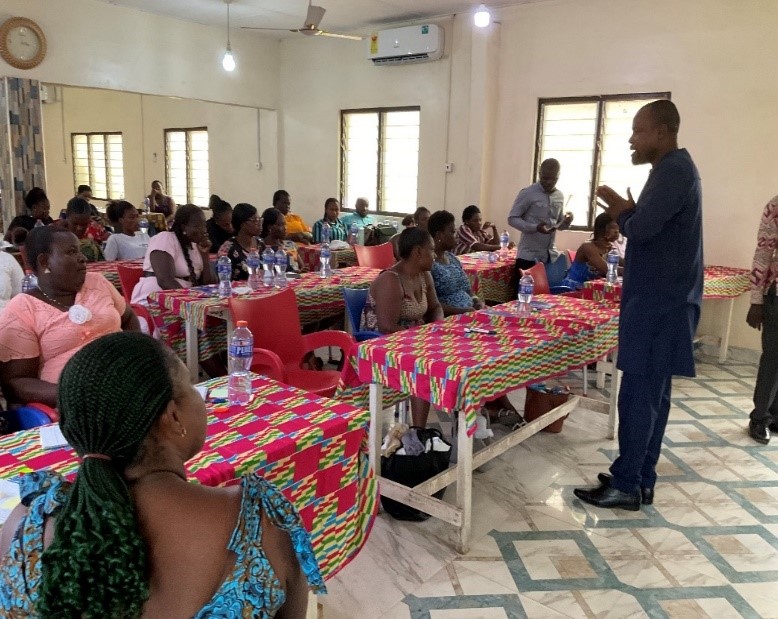



Trainees Contribution

The Enthusiastic Trainee Moments

Our Mentorship Moments


The Opening & Closing Ceremonies
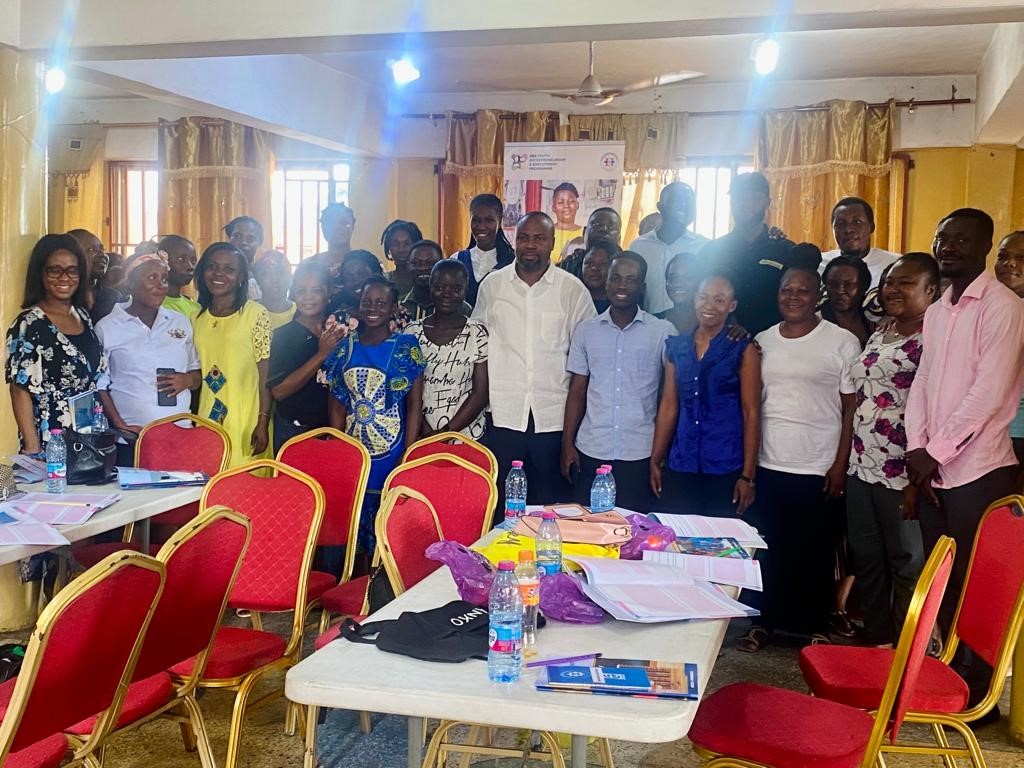



The Quality Control checks by Empretec, PWC, and GEA
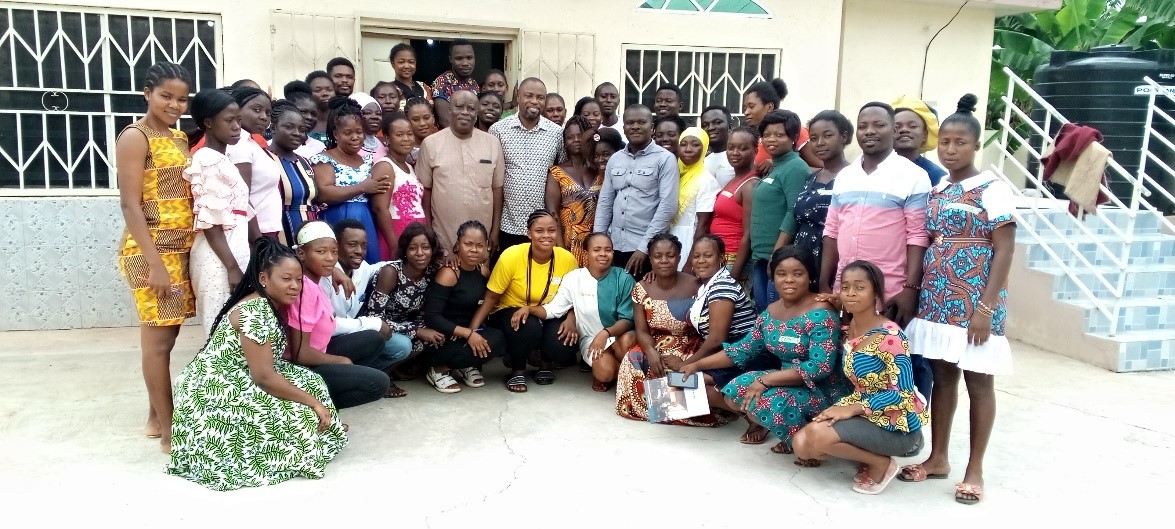
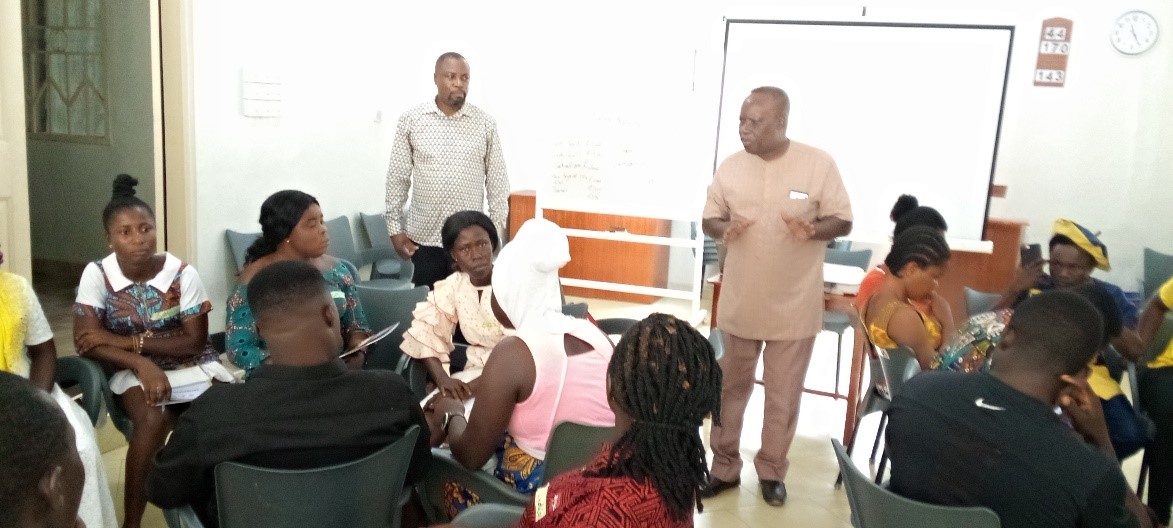


SSNIT, GRA and PWC with Us in Odumase


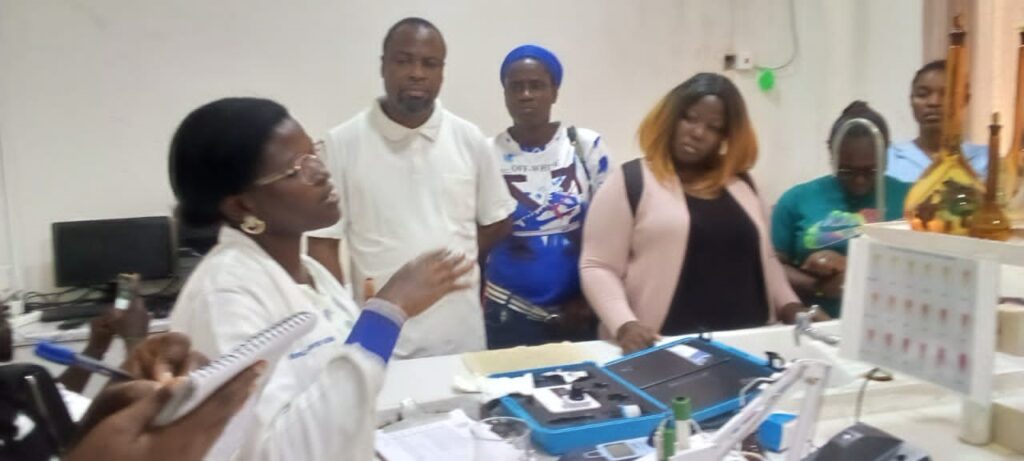
The Entry into Kpong Water Works


Our Galant Tour & KAIZEN at Kpong Water Works


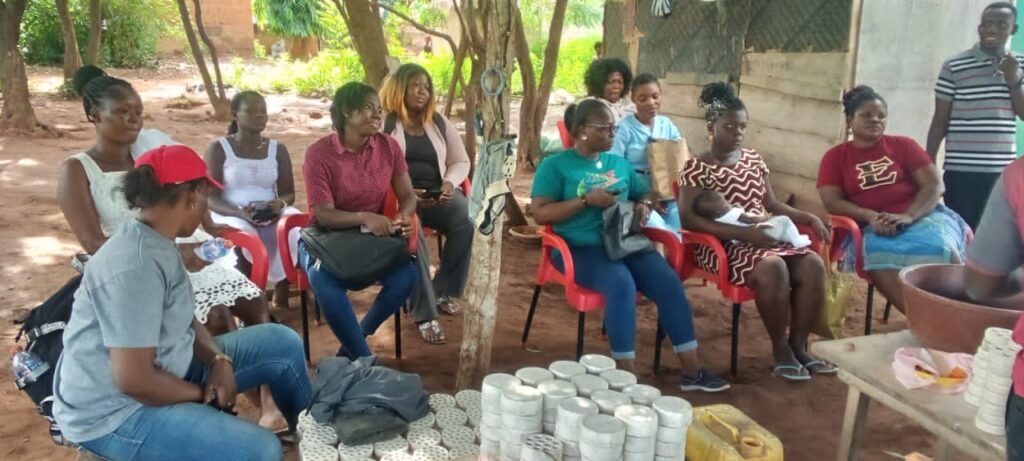
The Beads Making




Young entrepreneur in Training



